Degeneracy, W
Moderators: Chem_Mod, Chem_Admin
-
narek kurkjian 2I
- Posts: 35
- Joined: Mon Jan 09, 2023 9:25 am
-
Chem_Mod
- Posts: 23858
- Joined: Thu Aug 04, 2011 1:53 pm
- Has upvoted: 1253 times
Re: Degeneracy, W
In the Boltzmann's formula,
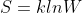
degeneracy, W, is the number (no units) of ways that particles in the system can be arranged with the same total energy. Each arrangement of particles is a different state called microstate, so W is the number of microstates that have the same energy. The idea behind this equation is that we can calculate entropy using the number of microstates.
If you remember from last quarter, I gave you a question about the particle in a two-dimensional box, and you listed out all the possible combinations of n_x and n_y values that yield the same energy-- that is degeneracy.
degeneracy, W, is the number (no units) of ways that particles in the system can be arranged with the same total energy. Each arrangement of particles is a different state called microstate, so W is the number of microstates that have the same energy. The idea behind this equation is that we can calculate entropy using the number of microstates.
If you remember from last quarter, I gave you a question about the particle in a two-dimensional box, and you listed out all the possible combinations of n_x and n_y values that yield the same energy-- that is degeneracy.
-
Casey Fineberg
- Posts: 34
- Joined: Mon Jan 03, 2022 9:55 am
Re: Degeneracy, W
Degeneracy is when you have 2 or more quantum states in a quantized energy level. For example, the p orbital has 3 degeneracies because it has 3 quantum states (3 orbitals of the same energy). And the d orbital has 5 degeneracies because it has 5 quantum states (five orbitals of the same energy).
-
Emily Lam 2H
- Posts: 36
- Joined: Mon Jan 09, 2023 9:20 am
Re: Degeneracy, W
Degeneracy is related to degenerate energy levels which is when an energy levels have more than one different quantum states. For example the degeneracy of p orbital is 3.
-
Emma MacLachlan 1D
- Posts: 42
- Joined: Mon Jan 09, 2023 2:35 am
- Been upvoted: 1 time
Re: Degeneracy, W
To add on, degeneracy can also be used to determine the positional or residual entropy of molecules when the temperature is 0K, or otherwise they are solid and not moving. For example: CO can be arranged as C=O or O=C, and therefore the residual entropy can be calculated as the number of states to the power of the number of particles.
-
Gianna McNiel 1I
- Posts: 49
- Joined: Mon Jan 09, 2023 8:27 am
Re: Degeneracy, W
Degeneracy is the number of possible positions that a molecule can have. W can be calculated by the number of positions to the n number of molecules. From this, the Boltzman equation can be used to calculate the entropy, based on this degeneracy (W) value. If degeneracy is higher, the entropy would also be higher.
-
Margreet Gawargious lecture 2 section 2H
- Posts: 34
- Joined: Mon Jan 09, 2023 9:19 am
Re: Degeneracy, W
Degeneracy is the total number of different possible states a molecule can be in while at the same energy. For example, the molecule CClH3 can be arranged in different ways, yet still have the same energy level. The number of different arrangements for CClH3 is called degeneracy.
Who is online
Users browsing this forum: No registered users and 6 guests

