During the test of an internal combustion engine, 3.00 L of nitrogen gas at 18.5 C was compressed suddenly (and irreversibly) to 0.500 L by driving in a piston. In the process, the temperature of the gas increased to 28.1 C. Assume ideal behavior. What is the change in entropy of the gas?
How can you use delta S = nRln(v2/v1) if the reaction is irreversible? Isn't this equation only applicable to reversible expansion?
9.13
Volume: 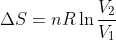
Temperature: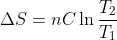
Temperature:
Moderators: Chem_Mod, Chem_Admin
-
Dhwani Krishnan 1G
- Posts: 63
- Joined: Fri Sep 28, 2018 12:17 am
-
Mukil_Pari_2I
- Posts: 87
- Joined: Fri Sep 28, 2018 12:29 am
Re: 9.13
Postby Mukil_Pari_2I » Sat Mar 16, 2019 12:17 am
Because you would have to calculate the entropy due to the temperature change, the reversible equation can be used for the first part. You would have to consider each portion separately. So, first you would assume the the temperature as constant (isothermal), for the compression. Then, you would assume the volume as constant when calculating the entropy for the temperature.
Return to “Entropy Changes Due to Changes in Volume and Temperature”
Jump to
- NEWS
- NEWS & RESOURCES
- About The Forum
- Forum Rules and Helpful Hints
- How to make a New Post (submit a question) and use Equation Editor (click for details)
- Email Notification (click for details)
- How to Subscribe to a Forum, Subscribe to a Topic, and Bookmark a Topic (click for details)
- Endorsed Post (click for details)
- Multimedia Attachments (click for details)
- Strikethrough (click for details)
- Chem 14A
- Review of Chemical & Physical Principles
- SI Units, Unit Conversions
- Significant Figures
- Accuracy, Precision, Mole, Other Definitions
- Molarity, Solutions, Dilutions
- Empirical & Molecular Formulas
- Balancing Chemical Reactions
- Limiting Reactant Calculations
- The Quantum World
- Properties of Light
- Properties of Electrons
- Einstein Equation
- *Black Body Radiation
- Photoelectric Effect
- Bohr Frequency Condition, H-Atom , Atomic Spectroscopy
- DeBroglie Equation
- Heisenberg Indeterminacy (Uncertainty) Equation
- *Shrodinger Equation
- *Particle in a Box
- Wave Functions and s-, p-, d-, f- Orbitals
- Quantum Numbers and The H-Atom
- Electron Configurations for Multi-Electron Atoms
- Trends in The Periodic Table
- Chemical Bonds
- Ionic & Covalent Bonds
- Sigma & Pi Bonds
- Lewis Structures
- Resonance Structures
- Formal Charge and Oxidation Numbers
- Octet Exceptions
- Coordinate Covalent Bonds
- Polarisability of Anions, The Polarizing Power of Cations
- Electronegativity
- Dipole Moments
- Bond Lengths & Energies
- Forces and Liquid Structure
- Interionic and Intermolecular Forces (Ion-Ion, Ion-Dipole, Dipole-Dipole, Dipole-Induced Dipole, Dispersion/Induced Dipole-Induced Dipole/London Forces, Hydrogen Bonding)
- *Liquid Structure (Viscosity, Surface Tension, Liquid Crystals, Ionic Liquids)
- Molecular Shape and Structure
- Determining Molecular Shape (VSEPR)
- Hybridization
- *Molecular Orbital Theory (Bond Order, Diamagnetism, Paramagnetism)
- Coordination Compounds and their Biological Importance
- Naming
- Shape, Structure, Coordination Number, Ligands
- Biological Examples
- Industrial Examples
- *Stereochemistry
- *Crystal Field Theory
- *Molecular Orbital Theory Applied To Transition Metals
- Acids and Bases
- Properties & Structures of Inorganic & Organic Acids
- Properties & Structures of Inorganic & Organic Bases
- Amphoteric Compounds
- Lewis Acids & Bases
- Bronsted Acids & Bases
- Conjugate Acids & Bases
- Acidity & Basicity Constants and The Conjugate Seesaw
- Calculating pH or pOH for Strong & Weak Acids & Bases
- Polyprotic Acids & Bases
- Identifying Acidic & Basic Salts
- Calculating the pH of Salt Solutions
- Air Pollution & Acid Rain
- Chem 14A Uploaded Files (Worksheets, etc.)
- Student Social/Study Group
- Administrative Questions and Class Announcements
- General Science Questions
- *Aqueous Equilibria
- *Making Buffers & Calculating Buffer pH (Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation)
- *Biological Importance of Buffer Solutions
- *Titrations & Titration Calculations
- *Indicators
- Chem 14B
- Chemical Equilibrium
- Ideal Gases
- Equilibrium Constants & Calculating Concentrations
- Non-Equilibrium Conditions & The Reaction Quotient
- Applying Le Chatelier's Principle to Changes in Chemical & Physical Conditions
- Thermochemistry
- Phase Changes & Related Calculations
- Reaction Enthalpies (e.g., Using Hess’s Law, Bond Enthalpies, Standard Enthalpies of Formation)
- Heat Capacities, Calorimeters & Calorimetry Calculations
- Thermodynamics
- Thermodynamic Systems (Open, Closed, Isolated)
- Thermodynamic Definitions (isochoric/isometric, isothermal, isobaric)
- Calculating Work of Expansion
- Concepts & Calculations Using First Law of Thermodynamics
- Concepts & Calculations Using Second Law of Thermodynamics
- Third Law of Thermodynamics (For a Unique Ground State (W=1): S -> 0 as T -> 0) and Calculations Using Boltzmann Equation for Entropy
- Entropy Changes Due to Changes in Volume and Temperature
- Calculating Standard Reaction Entropies (e.g. , Using Standard Molar Entropies)
- Gibbs Free Energy Concepts and Calculations
- Van't Hoff Equation
- Environment, Fossil Fuels, Alternative Fuels
- Biological Examples (*DNA Structural Transitions, etc.)
- Electrochemistry
- Balancing Redox Reactions
- Galvanic/Voltaic Cells, Calculating Standard Cell Potentials, Cell Diagrams
- Work, Gibbs Free Energy, Cell (Redox) Potentials
- Appications of the Nernst Equation (e.g., Concentration Cells, Non-Standard Cell Potentials, Calculating Equilibrium Constants and pH)
- Interesting Applications: Rechargeable Batteries (Cell Phones, Notebooks, Cars), Fuel Cells (Space Shuttle), Photovoltaic Cells (Solar Panels), Electrolysis, Rust
- Chemical Kinetics
- Kinetics vs. Thermodynamics Controlling a Reaction
- General Rate Laws
- Method of Initial Rates (To Determine n and k)
- Zero Order Reactions
- First Order Reactions
- Second Order Reactions
- Reaction Mechanisms, Reaction Profiles
- Arrhenius Equation, Activation Energies, Catalysts
- *Enzyme Kinetics
- Experimental Details
- Environment, Ozone, CFCs
- Biological Examples
- Chem 14B Uploaded Files (Worksheets, etc.)
- Student Social/Study Group
- Administrative Questions and Class Announcements
- General Science Questions
- *Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Organic Reactions
- *Electrophiles
- *Nucleophiles
- *Organic Reaction Mechanisms in General
- *Electrophilic Addition
- *Nucleophilic Substitution
- *Free Energy of Activation vs Activation Energy
- *Complex Reaction Coordinate Diagrams
- *Names and Structures of Organic Molecules
- *Alkanes
- *Cycloalkanes
- *Alkenes
- *Cycloalkenes
- *Alkynes
- *Constitutional and Geometric Isomers (cis, Z and trans, E)
- *Haloalkanes
- *Haloalkenes
- *Alcohols
- *Ethers
- *Aldehydes
- *Ketones
- *Carboxylic Acids
- *Amines
- *Identifying Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary Carbons, Hydrogens, Nitrogens
- *Conformations of Organic Molecules
- *Alkanes and Substituted Alkanes (Staggered, Eclipsed, Gauche, Anti, Newman Projections)
- *Cyclopropanes and Cyclobutanes
- *Cyclopentanes
- *Cyclohexanes (Chair, Boat, Geometric Isomers)
- *Calculations Using ΔG° = -RT ln K
- *ChemDraw
- *Chem3D
- Chem 14C/D Topics
- Resonance in Organic Compounds
- Stereochemistry in Organic Compounds (Chirality, Stereoisomers, R/S, d/l, Fischer Projections)
Who is online
Users browsing this forum: No registered users and 5 guests

