Can someone help with this question?
Suppose that 50.0 g of H20(l) at 20.0 C is mixed with 65.0g of H20(l) at 50.0 C at constant atmospheric pressure in a thermally insulted vessel. Calculate delta S and delta S tot for the process.
9.43
Moderators: Chem_Mod, Chem_Admin
-
Anh Nguyen 2A
- Posts: 36
- Joined: Fri Sep 29, 2017 7:05 am
- Been upvoted: 1 time
Re: 9.43
You set qhot=-qcold to calculate the final temperature of the system as this is a thermally insulated vessel. (q=m.C.deltaT)
deltaS total = deltaS of the hot water + deltaS of the cold water
Calculate deltaS of each using deltaS=m.C.ln(T2/T1)
deltaS total = deltaS of the hot water + deltaS of the cold water
Calculate deltaS of each using deltaS=m.C.ln(T2/T1)
-
Julian Krzysiak 2K
- Posts: 49
- Joined: Fri Sep 29, 2017 7:07 am
Re: 9.43
Because we need to know the entropy of both the system (20 C) and the surroundings (50 C), we need to use the equation for finding the entropy with the final and initial temperatures. Unfortunately, they don't give us the final Temperature, so we have to find it ourselves. So you set both of the equations equal to each other, using 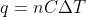 , and that will get you the final temperature ( Remember to set the "surroundings" as negative). Now you can solve the entropies for both the system and the surroundings now that we have the final and initial temperatures.
, and that will get you the final temperature ( Remember to set the "surroundings" as negative). Now you can solve the entropies for both the system and the surroundings now that we have the final and initial temperatures.
To calculate the Total Entropy, simply add both entropies together.
To calculate the Total Entropy, simply add both entropies together.
Return to “Calculating Standard Reaction Entropies (e.g. , Using Standard Molar Entropies)”
Who is online
Users browsing this forum: No registered users and 3 guests

