achieve number 7 week 2
Moderators: Chem_Mod, Chem_Admin
-
Isabella Nassir 2B
- Posts: 99
- Joined: Fri Sep 24, 2021 5:10 am
achieve number 7 week 2
HClO is a weak acid ( Ka=4.0×10−8 ) and so the salt NaClO acts as a weak base. What is the pH of a solution that is 0.028 M in NaClO at 25 °C?
-
Melinda Luo 2G
- Posts: 114
- Joined: Fri Sep 24, 2021 6:26 am
Re: achieve number 7 week 2
For this problem, assume that NaClO ionizes into Na+ and ClO-. Since a+ is a spectator ion, we can ignore it and focus solely on ClO-.
The chemical equation looks as follows:
ClO- + H2O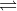 HClO + OH-
HClO + OH-
Since we are given Ka, we need to find the respective Kb value by dividing 10-14 by Ka. Then, set up the proper equilibrium equation to find the concentration of OH-.
Since the question is asking for pH, you can first find the pOH value and then subtract that value from 14, or divide 10-14 by the OH- and then use -log.
The chemical equation looks as follows:
ClO- + H2O
Since we are given Ka, we need to find the respective Kb value by dividing 10-14 by Ka. Then, set up the proper equilibrium equation to find the concentration of OH-.
Since the question is asking for pH, you can first find the pOH value and then subtract that value from 14, or divide 10-14 by the OH- and then use -log.
-
Aaron Kwan 3B
- Posts: 101
- Joined: Fri Sep 24, 2021 6:07 am
Re: achieve number 7 week 2
Make sure you figure out whether you can use the approximation to calculate x or not. If x is less than 5% of the initial 0.026, then the approximation is valid.
-
Harsimer Bal 3K
- Posts: 106
- Joined: Fri Sep 24, 2021 5:16 am
- Been upvoted: 1 time
Re: achieve number 7 week 2
Another way I like to think of which ion in the salt we will be focusing on in a reaction with water is by looking at which ion is the conjugate acid/base of a weak base/acid. In this problem, Na+ is the conjugate acid of a strong base NaOH and therefore its concentration does not change over the course of the reaction. ClO- is the conjugate base of a weak acid, HClO-, so its concentration will change as not all ClO- molecules will be protonated. Thus, the equation used is ClO- + H2O HClO + OH-.
-
Mia Glinn 1I
- Posts: 105
- Joined: Fri Sep 24, 2021 7:13 am
- Been upvoted: 1 time
Re: achieve number 7 week 2
Start by writing your reaction, which was stated above. Then you can use an ICE table to solve for X, which will allow you to find the concentration of OH-.
ClO- HClO OH-
I 0.05 0 0
C -X +X +X
E 0.05-X X X
*note my values were different in my problem*
Then you have to find the Kb using the Ka provided by using the formula Ka*Kb=Kw. Once you find Kb you can set that equal to X^2/0.05-X and solve for X. Use that solution to find the pOH (since we used Kb), and then convert that to pH using the formula pH+pOH=14.
ClO- HClO OH-
I 0.05 0 0
C -X +X +X
E 0.05-X X X
*note my values were different in my problem*
Then you have to find the Kb using the Ka provided by using the formula Ka*Kb=Kw. Once you find Kb you can set that equal to X^2/0.05-X and solve for X. Use that solution to find the pOH (since we used Kb), and then convert that to pH using the formula pH+pOH=14.
-
Sidney Shah 3H
- Posts: 100
- Joined: Fri Sep 24, 2021 5:47 am
- Been upvoted: 1 time
Re: achieve number 7 week 2
For this problem, start by looking at the weak base NaClO as we are given the concentration. Then, since it is a salt, it dissociates and we disregard Na+ as it is a spectator ion and only focus on ClO-.
Now you can proceed to use the equation ClO- + H2O --> HClO + OH-. Set up ICE table, and use relationship that Ka * Kb = Kw to solve for x concentration
Now you can proceed to use the equation ClO- + H2O --> HClO + OH-. Set up ICE table, and use relationship that Ka * Kb = Kw to solve for x concentration
Return to “Non-Equilibrium Conditions & The Reaction Quotient”
Who is online
Users browsing this forum: No registered users and 3 guests

